
Authentication vs. Authorization – how both concepts work hand in hand
The Basics: Authentication
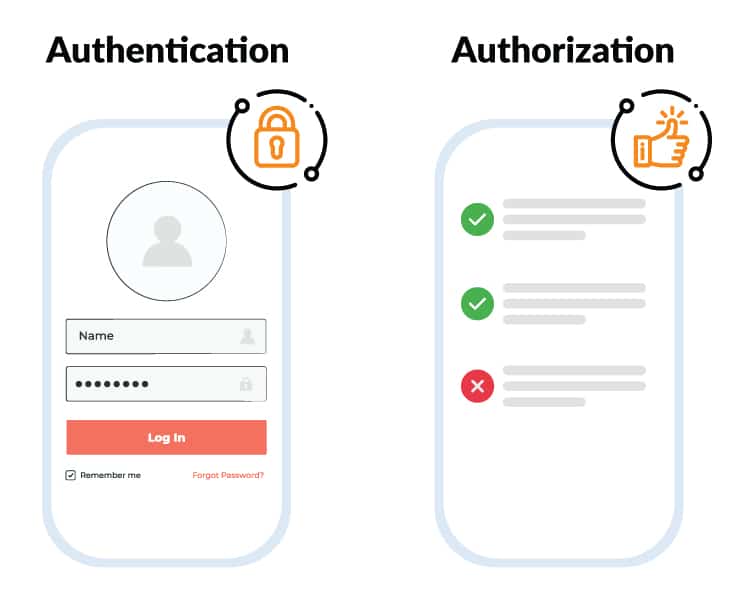
Think of authentication as the virtual bouncer standing at the entrance of a club. Its main goal is to verify your identity before granting access to the exclusive party inside. Authentication is the first line of defense that confirms you are who you claim to be. It typically involves providing a username and password combination, but it can also include other factors like biometrics (fingerprint or facial recognition) or security tokens. Users can choose from a variety of authentication methods for login, ranging from classic authentication via username and password to the much more convenient passwordless authentication, e.g. via biometric methods (Have a look at the passwordless authentication feature of the cidaas platform). Once you’ve successfully authenticated, the system knows that you are an approved user and will allow you to proceed to the next step. However, keep in mind that authentication alone does not grant you any special privileges or access control. That’s where authorization steps in.
The Power of Authorization
Authorization determines what actions or resources an authenticated user is allowed to access. It’s like the bouncer telling you which areas of the club you’re allowed to enter or what you can do once you’re inside. Authorization ensures that you can only access the parts of a resource, website or application that you have permission to use. For instance, let’s say you’ve successfully authenticated yourself as a registered user on an e-commerce website. Now, the authorization process determines whether you have the authority to view your order history, update your personal details, or make a purchase. Without proper authorization, these actions would be off-limits, ensuring that your sensitive data remains secure.
The Two Sides of the Coin
Now that we understand authentication and authorization individually, it’s important to note that they go hand in hand. Authentication is the process of verifying your identity, while authorization determines what you can do once your identity is confirmed. Both are essential in establishing a secure digital environment. Imagine a situation where authentication is skipped, and anyone can enter the club without proving their identity. This would jeopardize the safety of the attendees and possibly lead to unauthorized access to restricted areas. Similarly, without proper authorization, authenticated users are like guests who hasn’t access control to any part of the club, resulting in a frustrating user experience.
Authentication and Authorization features in cidaas
cidaas offers a wide range of functionalities to authenticate & authorise users. More than 14 different authentication methods are available with which users can log in. A sophisticated multi-factor authentication is also part of the cidaas platform and offers the possibility to verify users in a multi-step process with an additional factor. Multi-factor authentication can be used in a variety of ways, from a mandatory multi-factor to an intelligent multi-factor where the additional factor is only added when required, e.g. in the case of suspicious behavior or the use of another device. For example, one-time passwords (OTPs) play a crucial role in multifactor authentication (MFA). As these are limited and can only be used once for logging in, they increase the security of accounts and make a stolen password worthless. In addition to OTPs, biometrics, such as fingerprint or facescan, can reduce reliance on traditional passwords. The combination of one-time passwords and biometrics provides a robust security solution.
For authentication, the ID card can be used as a part of identity verification (link to ID vali.) to ensure that the person trying to access a system or application is indeed who they say they are.
The authentication is complemented by sophisticated authorization functionalities, so cidaas offers a flexible scope management with which authorizations can be controlled on application level. With the cidaas group and role management an authorization of users can be mapped over roles or over groups, which are assigned to the user. This extensive authorization management is not only interesting with regard to security, but also to map relationships, such as the different users of a family that are mapped with the roles, father, mother and child in a group for the family. Or also employees in relation to different teams.
Summary of Difference
Authentication and authorization are two pillars of cybersecurity that work in tandem to protect systems and your personal information online. Understanding the distinction between the two is crucial, as it empowers you to recognize the layers of security implemented by websites and applications. Next time you sign into an account or use an app, take a moment to appreciate the invisible yet powerful mechanisms at play. Authentication ensures that only you can enter the digital club, and authorization determines which party zones you’re allowed to access. So, remember, while authentication verifies your identity for access, authorization dictates your privileges. Together, they form a robust security framework that keeps your digital world safe. Stay secure, and happy browsing!
About cidaas
cidaas, the European cloud identity and access management system from Widas ID GmbH, delivers an out-of-the-box solution for federated identities, Single Sign-On and Multi-factor Authentication. With cidaas, companies create unique user identification and maximum security across all channels. Based on the standards OAuth2.0, OpenID and its “Everything is an API” architecture, cidaas can be seamlessly integrated into any software landscape and scales effortlessly up to many millions of users.
